Using an absolute antenna model, receiver antenna PCV as well as satellite antenna PCV values have to be applied. Receiver antenna PCV values are obtained from robot, anechoic chamber calibrations or field relative calibrations. Satellite antenna PCV are estimated in a data analysis of a global GNSS tracking network based on the receiver antenna PCV.
The Center for Orbit Determination in Europe (CODE) contributes to the estimation of the satellite antenna PCV. An antenna PCV consists of a constant part (offset) and a variable part (pattern). The satellite antenna offsets are estimated in a satellite fixed coordinate system, where the Z-direction points to the Earth. Estimated Z-offsets reach values between 0.5 m and 2.65 m for GPS satellites and between 1.80 m and 2.40 m for GLONASS satellites.
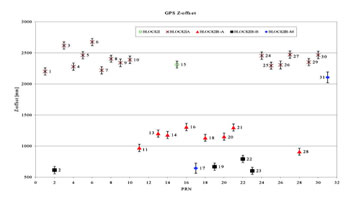
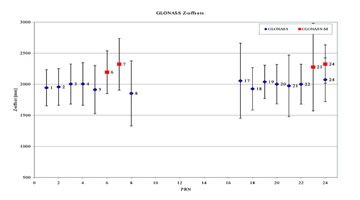 Figure 1: Satellite antenna Z-offsets for GPS and GLONASS satellites (estimated from 10 months of data in 2005 and 2006, error bars rescaled by a factor of five for plotting).
Figure 1: Satellite antenna Z-offsets for GPS and GLONASS satellites (estimated from 10 months of data in 2005 and 2006, error bars rescaled by a factor of five for plotting).
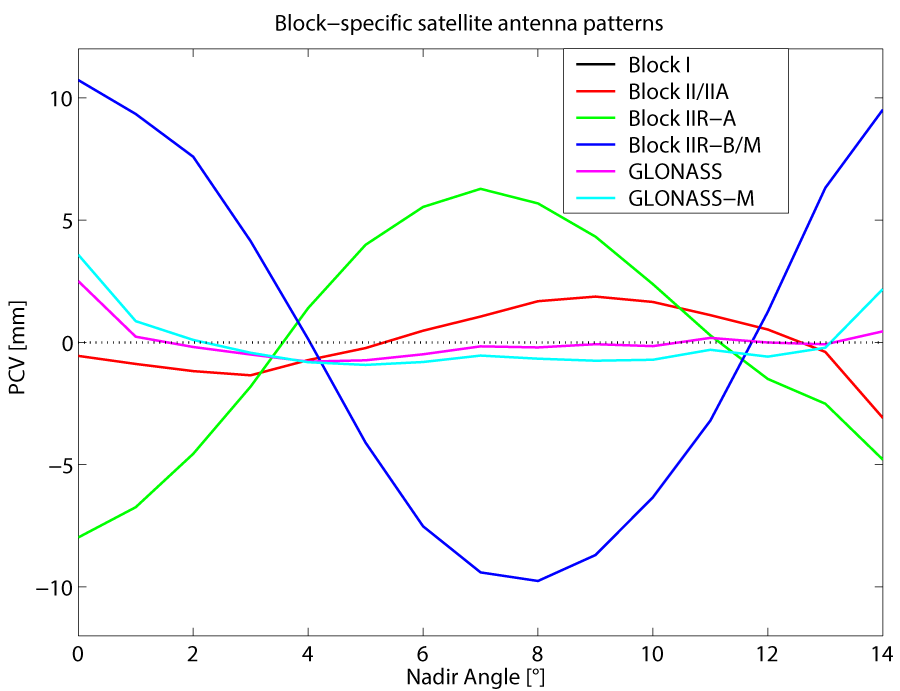 Figure 2: Satellite antenna pattern for GPS and GLONASS satellites (estimated from 10 months of data in 2005 and 2006).
Figure 2: Satellite antenna pattern for GPS and GLONASS satellites (estimated from 10 months of data in 2005 and 2006).
GPS satellite antenna patterns differ significantly from zero, whereas GLONASS satellite antenna patterns show a much lower variation.
Values of up to 1 cm for GPS satellites indicate that PCV values are not negligible for high precision positioning. All PCV values of receiver and satellite antennas are stored together in the ANTEX formatted file available on the IGS ftp server. This file is updated regularly when new receiver or satellite antenna values become available.